Embark on a scientific voyage with our prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells worksheet. Dive into the intricacies of cell biology, unraveling the fundamental differences that shape the diversity of life.
This comprehensive guide explores the structural components, genetic material, cell division, protein synthesis, metabolism, and evolutionary relationships between these two cell types. Prepare to delve into the fascinating world of cellular biology and expand your understanding of the building blocks of life.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
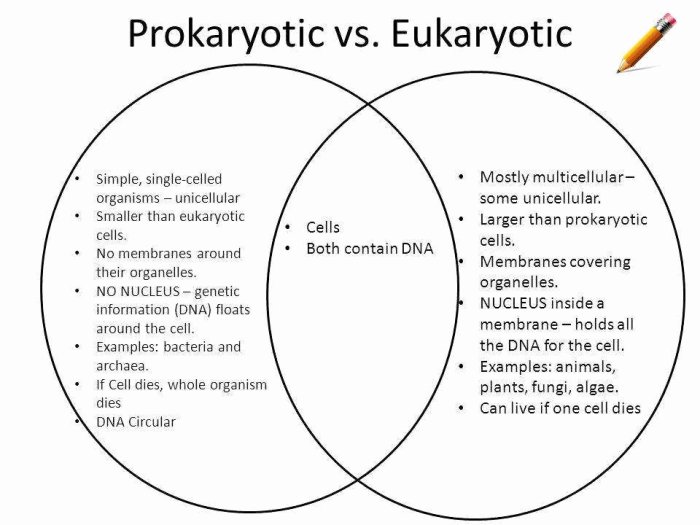
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and they lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and they are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells.
Cell Structure and Organization
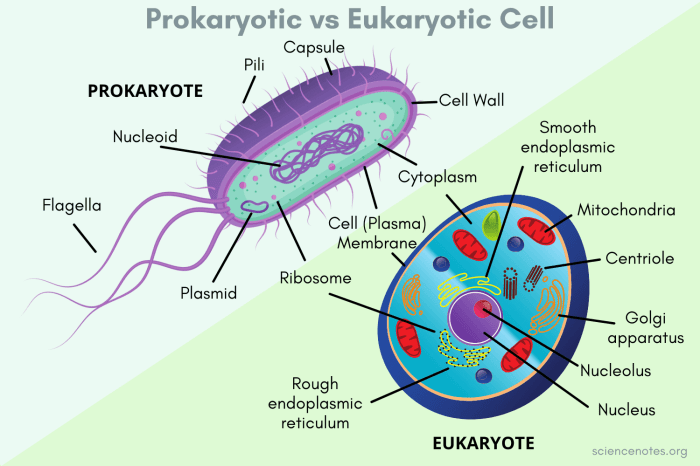
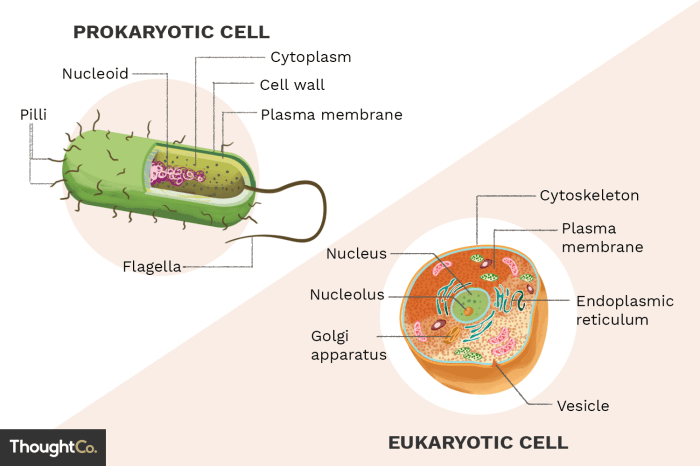
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ significantly in their structure and organization. Prokaryotic cells are typically 0.1-5.0 μm in size, while eukaryotic cells are typically 10-100 μm in size. Prokaryotic cells have a simple structure, with a single circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm.
They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a more complex structure, with a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
Table: Comparison of Structural Components of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells worksheet
| Component | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5.0 μm | 10-100 μm |
| Shape | Variable | Variable |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Chromosome | Single, circular | Multiple, linear |
Genetic Material
The genetic material of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is also different. Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have multiple, linear chromosomes located in the nucleus. The DNA of eukaryotic cells is also more complex than the DNA of prokaryotic cells, with introns and exons.
Introns are non-coding regions of DNA that are removed during the process of transcription, while exons are coding regions of DNA that are translated into proteins.
Cell Division
Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis and meiosis. Binary fission is a simple process in which the cell simply divides in two. Mitosis is a more complex process in which the chromosomes are duplicated and then separated into two new cells.
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells and results in the production of gametes.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis occurs in two steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into RNA. Translation is the process of using the RNA to synthesize proteins. In prokaryotic cells, transcription and translation occur in the cytoplasm.
In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Metabolism
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differ in their metabolism. Prokaryotic cells are typically more versatile in their metabolism than eukaryotic cells. They can use a wide variety of organic and inorganic compounds as sources of energy and carbon. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more specialized in their metabolism and typically require organic compounds as sources of energy and carbon.
Evolution and Diversity
Prokaryotic cells are the oldest type of cells on Earth, and they have evolved over billions of years. Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells about 2 billion years ago. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and they have a wider range of capabilities.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of habitats, from the depths of the ocean to the tops of mountains.
Essential Questionnaire: Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both.
How do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, a simple process where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are responsible for assembling amino acids into proteins, a fundamental process for all cells.