The double-entry accounting system records each transaction twice, providing a comprehensive and reliable method for tracking financial activities. This meticulous approach ensures the accuracy and integrity of financial data, making it a cornerstone of modern accounting practices.
The fundamental principles governing this system, including the use of debits and credits, ensure that every transaction has an equal and opposite entry. This approach creates a self-balancing ledger that facilitates error detection and enhances the overall reliability of the financial records.
Definition of Double-Entry Accounting System
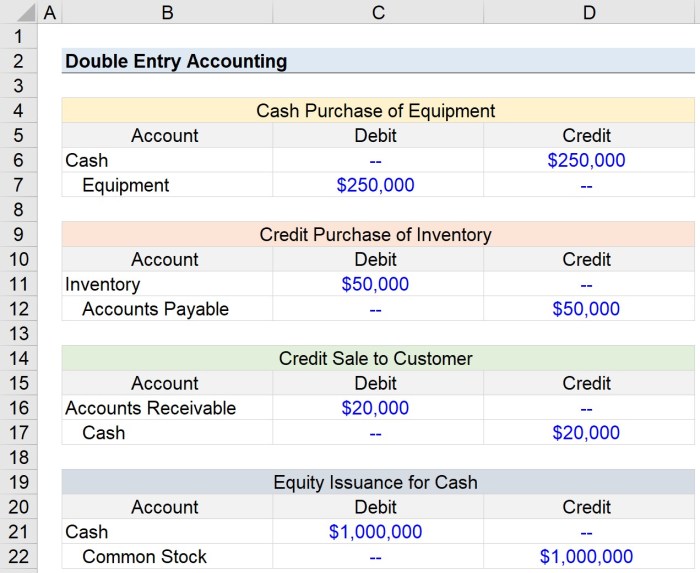
A double-entry accounting system is a method of recording financial transactions where each transaction is recorded twice, once as a debit and once as a credit. This ensures that the total debits are always equal to the total credits, providing a self-balancing system that enhances accuracy and reliability.
Principles of Double-Entry Accounting
The double-entry accounting system is governed by several fundamental principles, including:
- Debit-Credit Equality:Each transaction must have equal debits and credits.
- Dual Aspect:Every transaction affects at least two accounts.
- Balance Sheet Equation:Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Revenue and Expense Recognition:Revenue is recognized when earned, and expenses are recognized when incurred.
Advantages of Double-Entry Accounting
The double-entry accounting system offers several advantages, including:
- Accuracy:The system’s self-balancing nature helps minimize errors and ensures the accuracy of financial statements.
- Reliability:The dual aspect principle provides a comprehensive record of transactions, enhancing the reliability of financial information.
- Detection of Errors:Any errors in recording transactions will result in an imbalance between debits and credits, making them easier to detect and correct.
Limitations of Double-Entry Accounting
Despite its advantages, the double-entry accounting system also has some limitations:
- Complexity:The system can be complex to implement and maintain, especially for large organizations with numerous transactions.
- Time-Consuming:Recording each transaction twice can be time-consuming, particularly for manual accounting systems.
- Prone to Manipulation:While the system provides safeguards against errors, it is still possible for individuals to manipulate records to conceal financial irregularities.
Examples of Double-Entry Accounting
The following table illustrates how transactions are recorded twice in a double-entry accounting system:
| Transaction | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Purchased inventory for cash | Inventory | Cash |
| Sold inventory on account | Accounts Receivable | Inventory |
| Paid wages to employees | Wages Expense | Cash |
Applications of Double-Entry Accounting
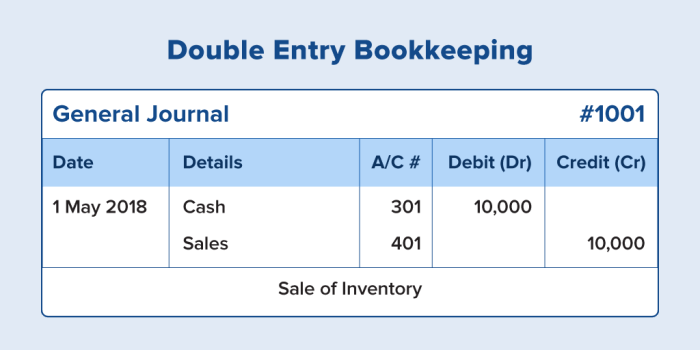
The double-entry accounting system is widely used in various industries and businesses, including:
- Corporations:Public and private companies use double-entry accounting to maintain accurate financial records for reporting and compliance purposes.
- Non-profit Organizations:Non-profits utilize double-entry accounting to track income and expenses for financial transparency and accountability.
- Small Businesses:Double-entry accounting helps small businesses manage their finances, monitor cash flow, and prepare financial statements.
Historical Development of Double-Entry Accounting

The double-entry accounting system has a long and rich history, dating back to the 13th century in Italy. Key milestones in its development include:
- 12th Century:The concept of double-entry bookkeeping emerges in Genoa, Italy.
- 1494:Luca Pacioli publishes “Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita,” which includes a description of the double-entry accounting system.
- 16th Century:The double-entry accounting system spreads throughout Europe and becomes the standard for financial record-keeping.
Modern Double-Entry Accounting Systems: The Double-entry Accounting System Records Each Transaction Twice
Technology has significantly influenced the use of double-entry accounting. Modern accounting software, such as QuickBooks and SAP, automates many of the tasks associated with double-entry bookkeeping, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Advantages:Automated systems save time, reduce errors, and provide real-time access to financial data.
- Disadvantages:The cost of implementing and maintaining accounting software can be significant, and there is still a risk of errors due to data entry or system malfunctions.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of recording each transaction twice in double-entry accounting?
The purpose is to ensure that every transaction has an equal and opposite entry, creating a self-balancing ledger that enhances accuracy and facilitates error detection.
What are the advantages of using a double-entry accounting system?
Double-entry accounting provides increased accuracy, enhanced reliability, improved financial reporting, and simplified error detection.
What are the limitations of double-entry accounting?
Double-entry accounting can be complex and time-consuming, and it requires skilled accountants to maintain the system effectively.