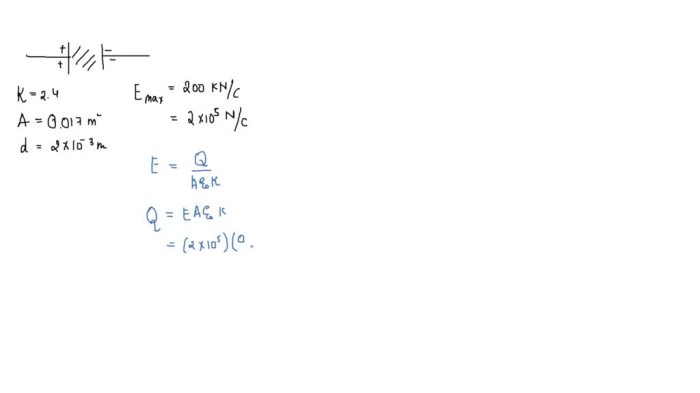A certain parallel plate capacitor, an essential component in the realm of electronics, embarks on an enlightening journey through its fundamental concepts, applications, and design intricacies. Prepare to delve into a world of electrical energy storage and manipulation as we unravel the secrets of this remarkable device.
From its fundamental structure to its diverse applications in electronic circuits, this guide will provide a comprehensive understanding of a certain parallel plate capacitor. Discover the factors that influence its capacitance, explore its energy storage capabilities, and witness its versatility in various electronic systems.
Definition and Basic Concepts

A parallel plate capacitor is a fundamental component in electrical circuits, consisting of two parallel conductive plates separated by a non-conducting dielectric material. Its primary function is to store electrical charge and release it when needed.
Capacitance, denoted by C, measures the ability of a capacitor to store charge. It is directly proportional to the plate area (A) and inversely proportional to the distance (d) between the plates:
C = ε0(A/d)
where ε 0is the permittivity of free space.
Capacitance and Charge Storage
Capacitance determines the amount of charge (Q) a capacitor can store. The relationship between charge and capacitance is:
Q = CV
where V is the voltage across the capacitor.
The capacitance of a capacitor is affected by the permittivity of the dielectric material and the dimensions of the plates.
Example:A parallel plate capacitor with plate area of 0.01 m 2and plate separation of 0.001 m has a capacitance of 8.85 x 10 -12F.
Energy Storage and Discharge, A certain parallel plate capacitor
A capacitor stores electrical energy (E) given by:
E = (1/2)CV2
When a capacitor is charged, energy is transferred to the electric field between the plates. When discharged, this energy is released.
Capacitor discharge involves releasing stored energy through a circuit. The time constant (τ) of the discharge process is determined by the capacitance and the resistance in the circuit.
Types and Applications
Parallel plate capacitors come in various types, including:
- Ceramic capacitors:High capacitance, small size, and low cost.
- Electrolytic capacitors:High capacitance, but larger size and polarized.
- Film capacitors:Moderate capacitance, good stability, and high voltage tolerance.
Applications of parallel plate capacitors include:
- Energy storage:In flashlights, defibrillators, and power supplies.
- Filtering:In power supplies to remove voltage fluctuations.
- Timing circuits:In clocks and electronic circuits.
Design and Fabrication
Designing a parallel plate capacitor involves considering:
- Capacitance requirement
- Voltage rating
- Size and shape constraints
Fabrication methods include:
- Metal deposition:Plates are deposited on a dielectric substrate.
- Winding:Plates are formed by winding conductive material around a core.
- Stacking:Plates are stacked with dielectric layers in between.
Electrical Properties
Electrical properties of a parallel plate capacitor include:
- Capacitance:As discussed earlier.
- Impedance:Z = 1/(2πfC), where f is the frequency.
- Equivalent circuit:A parallel combination of capacitance and resistance.
These properties affect the capacitor’s behavior in AC and DC circuits.
Example:In an AC circuit, a capacitor’s impedance decreases with increasing frequency, allowing more current to flow.
Applications in Electronics
Parallel plate capacitors are used in various electronic circuits, such as:
- Filtering:In power supplies to smooth voltage fluctuations.
- Timing circuits:In oscillators and clocks.
- Energy storage:In backup power supplies and energy-efficient devices.
Example:In a filter circuit, a capacitor in parallel with a resistor forms a low-pass filter, allowing low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency signals.
Top FAQs: A Certain Parallel Plate Capacitor
What is the primary function of a certain parallel plate capacitor?
A certain parallel plate capacitor primarily serves as an electrical energy storage device, capable of accumulating and releasing electrical charge.
How does the capacitance of a certain parallel plate capacitor affect its performance?
Capacitance, measured in Farads, determines the amount of charge a certain parallel plate capacitor can store. A higher capacitance allows for greater charge storage.
What factors influence the capacitance of a certain parallel plate capacitor?
Capacitance is influenced by the plate area, distance between plates, and the dielectric material used between the plates.
Can a certain parallel plate capacitor store both AC and DC currents?
Yes, a certain parallel plate capacitor can store both AC and DC currents. However, its behavior differs in each case due to its capacitive reactance.