Embark on a scientific exploration with our comprehensive ecological succession lab answer key PDF. This invaluable resource unveils the intricacies of ecosystem dynamics, guiding you through the fascinating stages of ecological succession and empowering you with a deeper understanding of the natural world.
Delve into the methodologies and procedures employed in ecological succession labs, gaining insights into data collection techniques, statistical analysis, and the interpretation of results. Witness the transformative power of ecological succession firsthand through meticulously documented observations and discover the factors that shape and influence these dynamic processes.
Ecological Succession Lab Overview

Ecological succession refers to the predictable and gradual changes in the species composition and structure of an ecological community over time. It plays a pivotal role in ecosystem dynamics, driving changes in ecosystem function, biodiversity, and stability.
There are three main types of ecological succession:
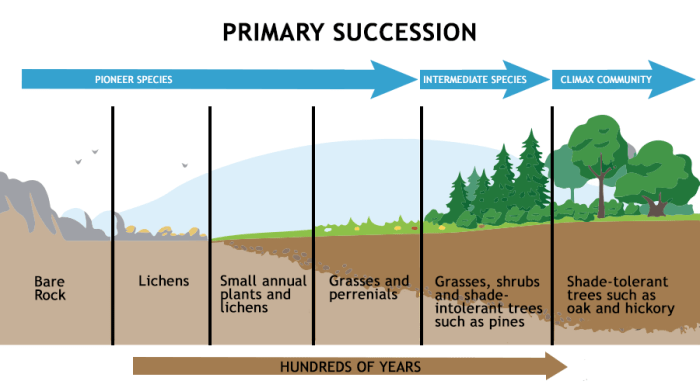
- Primary succession: Occurs on newly exposed or barren landforms, such as volcanic islands or glacial moraines.
- Secondary succession: Occurs in areas where an existing community has been disturbed, but the soil remains intact. Examples include abandoned agricultural fields or burned forests.
- Autogenic succession: Occurs when a change in the environment is caused by the organisms themselves. An example is the formation of peatlands, where the accumulation of organic matter alters the hydrology and soil chemistry.
Ecological succession typically proceeds through a series of stages, including pioneer species establishment, competition, and community stabilization. Each stage is characterized by distinct species assemblages and environmental conditions.
Methods and Procedures for Ecological Succession Lab
The ecological succession lab involves establishing study plots in areas undergoing ecological succession. Vegetation sampling is conducted periodically to track changes in species composition, abundance, and diversity. Environmental measurements, such as soil moisture, temperature, and light availability, are also collected to determine the factors influencing succession.
The data collected is analyzed using statistical techniques to identify patterns and relationships between vegetation and environmental variables. This helps researchers understand the mechanisms driving ecological succession and predict future changes in the community.
Results and Observations from Ecological Succession Lab, Ecological succession lab answer key pdf
The vegetation data collected during the lab reveals changes in species composition over time. Pioneer species, such as grasses and herbs, typically dominate the early stages of succession, followed by shrubs and trees in later stages.
The analysis of environmental data shows that factors such as soil moisture, temperature, and light availability influence the rate and direction of succession. For example, higher soil moisture favors the establishment of hydrophilic species, while increased light availability promotes the growth of shade-intolerant plants.
| Successional Stage | Dominant Species | Environmental Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Pioneer | Grasses, herbs | High light, low moisture |
| Intermediate | Shrubs, young trees | Moderate light, moisture |
| Climax | Mature trees | Low light, high moisture |
Discussion and Interpretation of Ecological Succession Lab Results
The results of the ecological succession lab provide insights into the theories of ecological succession. The observed patterns of species replacement and community development support the idea of predictable and directional changes in ecological communities over time.
The study highlights the importance of environmental factors in shaping ecological succession. It demonstrates that changes in soil moisture, temperature, and light availability can influence the composition and structure of the community.
- The lab has implications for understanding ecosystem dynamics and conservation. By studying ecological succession, we can predict how ecosystems will respond to disturbances and climate change.
- The lab has limitations, such as the relatively short time scale of the study. Long-term monitoring is necessary to fully understand the dynamics of ecological succession.
- Future research should focus on investigating the role of biotic interactions, such as competition and facilitation, in driving ecological succession.
FAQ Resource: Ecological Succession Lab Answer Key Pdf
What is the significance of ecological succession in ecosystem dynamics?
Ecological succession plays a pivotal role in shaping and maintaining the composition, structure, and function of ecosystems over time.
How do the different types of ecological succession vary?
Primary succession occurs on newly exposed or created substrates, while secondary succession follows disturbances that remove or alter the existing vegetation.
What are the key stages involved in ecological succession?
Ecological succession typically progresses through stages of pioneer species establishment, community development, and climax community formation.