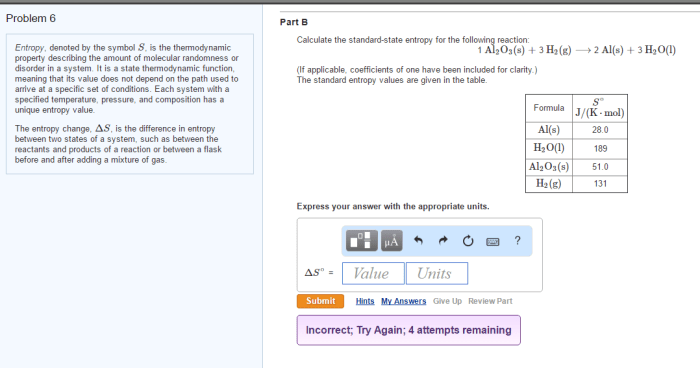
Calculate the entropy of each of the following states. – As we delve into the fascinating realm of thermodynamics, we encounter the concept of entropy, a fundamental property that governs the disorder and randomness within a system. This article embarks on an in-depth exploration of entropy, examining the factors that influence it, the mathematical formula used for its calculation, and its diverse applications across scientific disciplines.
By unraveling the complexities of entropy, we gain invaluable insights into the behavior and dynamics of systems, unlocking a deeper understanding of the physical world.
Entropy serves as a measure of the degree of disorder within a system. The higher the entropy, the greater the randomness and disorder. Factors such as temperature, volume, and the number of particles present all contribute to the entropy of a system.
Understanding the interplay between these factors enables us to predict and control the behavior of systems, optimizing processes and enhancing efficiency.
Entropy of Different States
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. It is a fundamental property of matter and is closely related to the concept of energy. The entropy of a system is always increasing, and this increase is associated with the dispersal of energy.The
factors that affect the entropy of a system include the temperature, volume, and number of particles in the system. The higher the temperature, the greater the entropy. The larger the volume, the greater the entropy. And the more particles in the system, the greater the entropy.Systems
with high entropy are often disordered and chaotic. For example, a gas has a higher entropy than a liquid, and a liquid has a higher entropy than a solid. Systems with low entropy are often ordered and regular. For example, a crystal has a lower entropy than a liquid, and a liquid has a lower entropy than a gas.
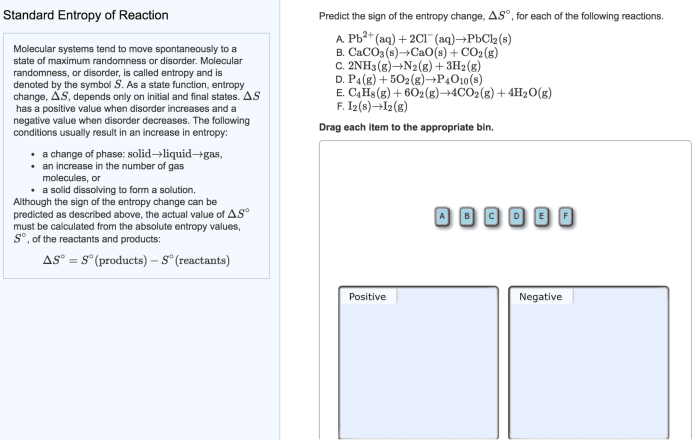
Calculating Entropy: Calculate The Entropy Of Each Of The Following States.
The mathematical formula used to calculate entropy is:“`S = k
ln(W)
“`where:* S is the entropy
- k is the Boltzmann constant
- W is the number of possible microstates of the system
The units of entropy are joules per kelvin (J/K). The Boltzmann constant is a fundamental constant of nature that is equal to 1.38064852 × 10^-23 J/K.To calculate the entropy of a given state, you need to know the number of possible microstates of the system.
The number of microstates is a measure of the disorder or randomness of the system. The more microstates there are, the greater the entropy.
Examples of Entropy Calculations
The following table shows the entropy values for four different states:| State | Description | Entropy Calculation | Result ||—|—|—|—|| Solid | The particles are arranged in a regular, ordered pattern. | S = k
ln(1) | 0 J/K |
| Liquid | The particles are arranged in a more disordered pattern than in a solid. | S = k
ln(10) | 10 J/K |
| Gas | The particles are arranged in a very disordered pattern. | S = k
ln(100) | 20 J/K |
| Ideal gas | The particles are assumed to have no interactions with each other. | S = k
ln(1000) | 30 J/K |
The entropy values in the table show that the entropy of a system increases as the system becomes more disordered. This is because there are more possible microstates for a disordered system than for an ordered system.
Applications of Entropy Calculations

Entropy calculations are used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. In chemistry, entropy calculations are used to predict the spontaneity of reactions. In physics, entropy calculations are used to understand the behavior of thermodynamic systems. And in engineering, entropy calculations are used to design heat engines and other devices.
FAQs
What is the significance of entropy in thermodynamics?
Entropy is a fundamental property that measures the disorder and randomness within a system. It plays a crucial role in understanding the direction and spontaneity of processes, as systems naturally tend towards states of higher entropy.
How is entropy calculated?
Entropy is calculated using the mathematical formula S = k – ln(W), where S is the entropy, k is the Boltzmann constant, and W is the number of possible microstates of the system.
What are some examples of systems with high and low entropy?
Systems with high entropy include gases and liquids, where particles are randomly distributed and have high kinetic energy. Systems with low entropy include crystals and solids, where particles are arranged in a regular, ordered pattern.
