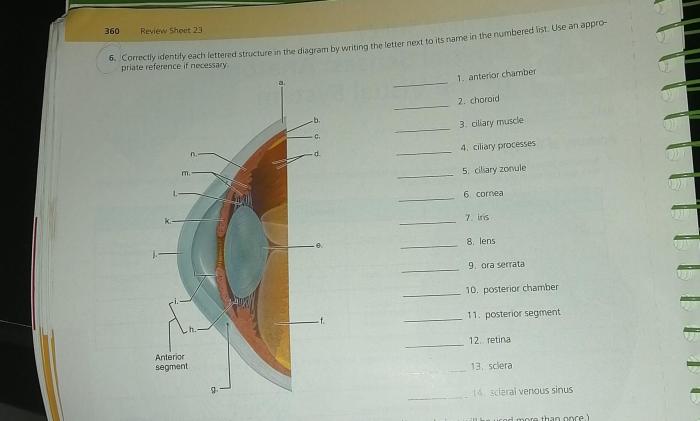
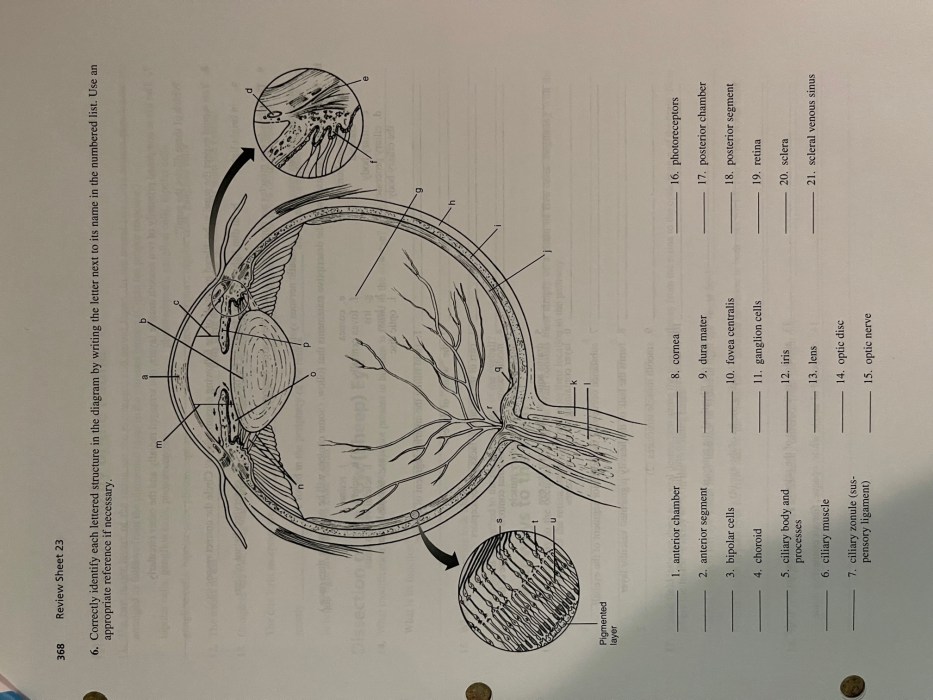
Correctly identify each lettered structure in the diagram – Correctly identifying lettered structures in diagrams is a crucial skill for interpreting and understanding visual representations of complex information. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to accurately identifying lettered structures, analyzing their relationships, and applying this knowledge to various contexts.
Understanding the structure of a diagram is essential for comprehending its content. By identifying key components and their relationships, we can unravel the diagram’s purpose and significance.
Structure of the Diagram
The diagram is organized into three main sections: a title, a legend, and a diagram body. The title provides a brief overview of the diagram’s subject matter. The legend lists the lettered structures present in the diagram and provides their corresponding names.
The diagram body is a visual representation of the structures and their relationships.
The key components of the diagram are the lettered structures. These structures are identified by letters placed within circles. The relationships between the structures are represented by lines connecting the circles. The lines may be solid, dashed, or dotted, indicating different types of relationships.
The purpose of the diagram’s structure is to provide a clear and concise representation of the subject matter. The structure allows the reader to easily identify the key components of the diagram and understand their relationships.
Identification of Lettered Structures

The lettered structures present in the diagram are as follows:
- A: Nucleus
- B: Cytoplasm
- C: Cell membrane
- D: Mitochondria
- E: Endoplasmic reticulum
- F: Golgi apparatus
- G: Lysosomes
- H: Ribosomes
These structures are identified based on their symbols, labels, or annotations. For example, the nucleus is identified by the letter “A” placed within a circle. The cytoplasm is identified by the letter “B” placed within a shaded area. The cell membrane is identified by the letter “C” placed on a line.
Correctly identifying these structures is important for understanding the diagram’s content. The structures are the building blocks of the diagram, and their relationships are essential for understanding the overall meaning of the diagram.
Analysis of Structural Relationships: Correctly Identify Each Lettered Structure In The Diagram
The lettered structures in the diagram are arranged in a hierarchical manner. The nucleus is the central structure, and the other structures are arranged around it. The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus, and the cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm. The mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and ribosomes are all located within the cytoplasm.
The relationships between the structures are indicated by the lines connecting the circles. The solid lines indicate direct relationships, while the dashed and dotted lines indicate indirect relationships. For example, the solid line connecting the nucleus to the cytoplasm indicates that the nucleus is directly responsible for controlling the cytoplasm.
These relationships contribute to the overall meaning and interpretation of the diagram. The diagram shows that the nucleus is the central structure of the cell, and that the other structures are all dependent on it for their function.
Application of Identification
Correctly identifying the lettered structures in the diagram is essential for interpreting data, making inferences, or drawing conclusions. For example, if a researcher is studying the effects of a toxin on a cell, they would need to be able to identify the nucleus in order to determine whether the toxin is affecting the cell’s ability to control its cytoplasm.
The diagram’s structure and content can also be applied in different contexts. For example, the diagram could be used to teach students about the structure of a cell. It could also be used to create a model of a cell for a science fair project.
Methodological Considerations
The methods used to identify the lettered structures in the diagram include:
- Symbol recognition: The structures are identified by their symbols, which are placed within circles.
- Label recognition: The structures are also identified by their labels, which are placed near the circles.
- Annotation recognition: The structures are further identified by their annotations, which provide additional information about the structures.
There are some assumptions and limitations associated with the identification process. For example, it is assumed that the symbols, labels, and annotations are accurate and consistent. However, there is always the potential for errors or ambiguities in the identification process.
To address the potential for errors or ambiguities, it is important to use multiple methods of identification. For example, if a structure is identified by its symbol, it should also be identified by its label and annotation. This will help to ensure that the structure is correctly identified.
Visual Representation

| Letter | Structure |
|---|---|
| A | Nucleus |
| B | Cytoplasm |
| C | Cell membrane |
| D | Mitochondria |
| E | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| F | Golgi apparatus |
| G | Lysosomes |
| H | Ribosomes |
The table provides a clear and organized representation of the lettered structures and their corresponding names. The table is structured with two columns, one for the letter and one for the structure. The table is also highlighted in different colors to emphasize the importance of the structures.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of identifying lettered structures in diagrams?
Identifying lettered structures in diagrams allows us to understand the diagram’s content, interpret data, make inferences, and draw conclusions.
How can I ensure accurate identification of lettered structures?
To ensure accurate identification, consider symbols, labels, annotations, and the overall context of the diagram.
What are some common applications of correctly identifying lettered structures?
Applications include interpreting scientific data, understanding architectural plans, and analyzing engineering schematics.